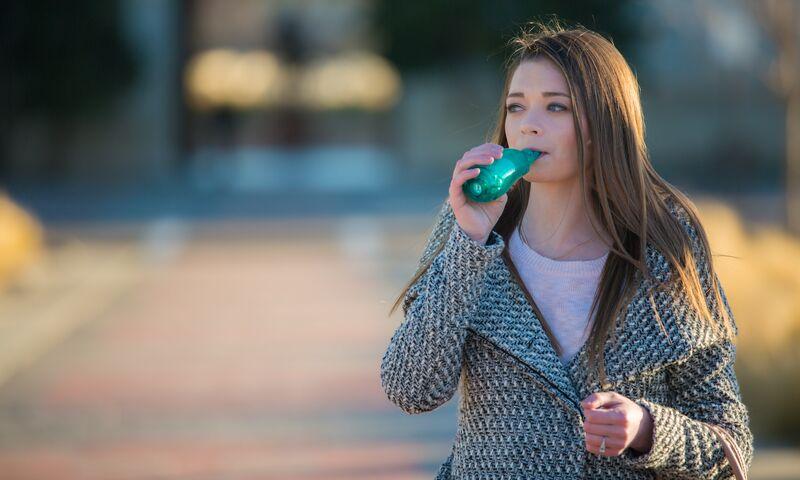Institution
Croatian Society for Cardiorespiratory Physiotherapy; Croatian thoracic society, Special hospital for pulmonary diseases, Zagreb; Clinic for pulmonary diseases Jordanovac, Zagreb
Institution Typology
Hospital
Country
Croatia
Description
BREATHING AGAINST RESISTANCE (PEP THERAPY Positive expiratory pressure)
The benefits of incorporating Positive Expiratory Pressure (PEP) therapy into the management of respiratory infections, including those caused by SARS-CoV-2, can be numerous and significant.
Improved Airway Clearance: PEP therapy helps mobilize secretions and mucus from the airways, facilitating their removal through coughing or suctioning. This can prevent mucus plugging, reduce the risk of atelectasis (lung collapse), and improve ventilation-perfusion matching, ultimately enhancing gas exchange and respiratory function.
Enhanced Lung Expansion: By promoting deep breathing and lung inflation during therapy sessions, PEP therapy can improve lung compliance and prevent or alleviate areas of lung collapse or consolidation commonly seen in respiratory infections. This can help maintain lung volume, prevent respiratory muscle weakness, and reduce the risk of complications such as pneumonia or respiratory failure.
Reduction of Respiratory Symptoms: PEP therapy can alleviate common respiratory symptoms associated with respiratory infections, including cough, dyspnea (shortness of breath), and chest congestion. By clearing mucus and improving airway patency, patients may experience relief from respiratory distress and discomfort, leading to improved overall quality of life.
Prevention of Complications: Effective airway clearance and lung expansion with PEP therapy can help prevent complications such as respiratory infections, exacerbations of underlying lung conditions (e.g., chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), and secondary bacterial pneumonia, which are common in patients with respiratory infections like SARS-CoV-2.
Facilitation of Respiratory Rehabilitation: PEP therapy can be an integral component of respiratory rehabilitation programs aimed at optimizing respiratory function, restoring physical capacity, and promoting functional independence in patients recovering from respiratory infections. By improving airway clearance and lung mechanics, PEP therapy can enhance the effectiveness of other rehabilitation interventions, such as exercise training and breathing exercises.
Potential Reduction in Hospital Length of Stay: By promoting effective airway clearance and respiratory function, PEP therapy may contribute to shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times for patients with respiratory infections, including those hospitalized with severe COVID-19.
Disease
Covid19
Activity level
Low
Activity Typology
Rehabilitation section-based activities
Motivation Tools
Not available